What is JWT?
JWT(JSON Web Token) is a token format. It is digitally-signed, self-contained, and compact. It provides a convenient mechanism for transferring data. JWT is not inherently secure, but the use of JWT can ensure the authenticity of the message so long as the signature is verified and the integrity of the payload can be guaranteed. JWT is often used for stateless authentication in simple use cases involving non-complex systems.
Here's an example of JWT:
eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJlbWFpbCI6Im9sYXR1bmRlZ2FydWJhQGdtYWlsLmNvbSIsImNow, let's authenticate/protect some routes.
Pre-requisites:
- Basic knowledge of HTML/JavaScript
- NodeJS should be installed in your system.
- express module for creating the server.
- mongoose module for MongoDB connection and queries.
- bcrypt module for hashing.
you can install all required packages by using following command:
npm install express mongoose bcrypt --saveStep 1. First, create a directory structure as below :
JWTApp
-api
--models
----userModel.js
--controllers
----userController.js
--route
----userRoute.js
--server.jsStep 2. Install “jsonwebtoken” packageby using following command
npm install jsonwebtoken -- saveStep 3. Create the user model
In the api/models folder, create a file called user userModel.js by running touch api/models/userModel.js.
In this file, create a mongoose schema with the following properties:
- fullName
- email address
- password
- the created date
Add the following code
'use strict';
var mongoose = require('mongoose'),
bcrypt = require('bcrypt'),
Schema = mongoose.Schema;
/**
* User Schema
*/
var UserSchema = new Schema({
fullName: {
type: String,
trim: true,
required: true
},
email: {
type: String,
unique: true,
lowercase: true,
trim: true,
required: true
},
hash_password: {
type: String
},
created: {
type: Date,
default: Date.now
}
});
UserSchema.methods.comparePassword = function(password) {
return bcrypt.compareSync(password, this.hash_password);
};
mongoose.model('User', UserSchema);Step 4. Create the user handlers
In the api/controllers folder, create a file called user userController.js by running touch api/controllers/userController.js
In the userController file, create three different handlers to handle by using the following code
'use strict';
var mongoose = require('mongoose'),
jwt = require('jsonwebtoken'),
bcrypt = require('bcrypt'),
User = mongoose.model('User');
exports.register = function(req, res) {
var newUser = new User(req.body);
newUser.hash_password = bcrypt.hashSync(req.body.password, 10);
newUser.save(function(err, user) {
if (err) {
return res.status(400).send({
message: err
});
} else {
user.hash_password = undefined;
return res.json(user);
}
});
};
exports.sign_in = function(req, res) {
User.findOne({
email: req.body.email
}, function(err, user) {
if (err) throw err;
if (!user || !user.comparePassword(req.body.password)) {
return res.status(401).json({ message: 'Authentication failed. Invalid user or password.' });
}
return res.json({ token: jwt.sign({ email: user.email, fullName: user.fullName, _id: user._id }, 'RESTFULAPIs') });
});
};
exports.loginRequired = function(req, res, next) {
if (req.user) {
next();
} else {
return res.status(401).json({ message: 'Unauthorized user!!' });
}
};
exports.profile = function(req, res, next) {
if (req.user) {
res.send(req.user);
next();
}
else {
return res.status(401).json({ message: 'Invalid token' });
}
};Note: A hash password was saved in the database using bcrypt.
Step 6. In the api/route folder, create a file called user userRoute.js and add the following code:
'use strict';
module.exports = function(app) {
var userHandlers = require('../controllers/userController.js');
// todoList Routes
app.route('/tasks')
.post(userHandlers.loginRequired, userHandlers.profile);
app.route('/auth/register')
.post(userHandlers.register);
app.route('/auth/sign_in')
.post(userHandlers.sign_in);
};Step 7. Add the following code in server.js
'use strict';
var express = require('express'),
app = express(),
port = process.env.PORT || 3000,
User = require('./api/models/userModel'),
bodyParser = require('body-parser'),
jsonwebtoken = require("jsonwebtoken");
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const option = {
socketTimeoutMS: 30000,
keepAlive: true,
reconnectTries: 30000
};
const mongoURI = process.env.MONGODB_URI;
mongoose.connect('mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017/?compressors=disabled&gssapiServiceName=mongodb', option).then(function(){
//connected successfully
}, function(err) {
//err handle
});
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: true }));
app.use(bodyParser.json());
app.use(function(req, res, next) {
if (req.headers && req.headers.authorization && req.headers.authorization.split(' ')[0] === 'JWT') {
jsonwebtoken.verify(req.headers.authorization.split(' ')[1], 'RESTFULAPIs', function(err, decode) {
if (err) req.user = undefined;
req.user = decode;
next();
});
} else {
req.user = undefined;
next();
}
});
var routes = require('./api/routes/userRoutes');
routes(app);
app.use(function(req, res) {
res.status(404).send({ url: req.originalUrl + ' not found' })
});
app.listen(port);
console.log(' RESTful API server started on: ' + port);
module.exports = app;Step 9. Now you just need to run the project by using the following command and try logging by using the JWT.
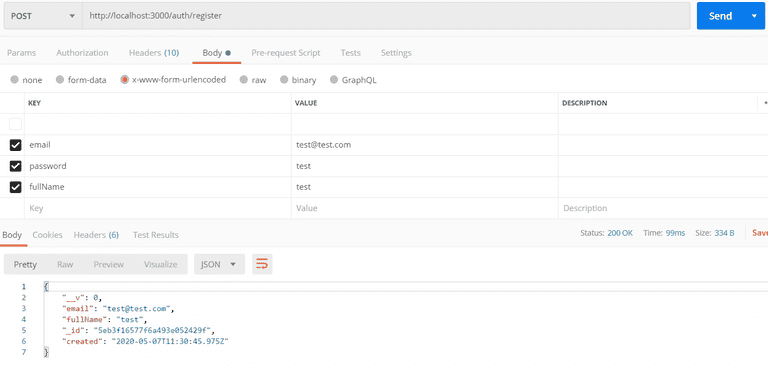
npm startStep 10. Open Postman and create a post request to localhost:3000/auth/register as below:
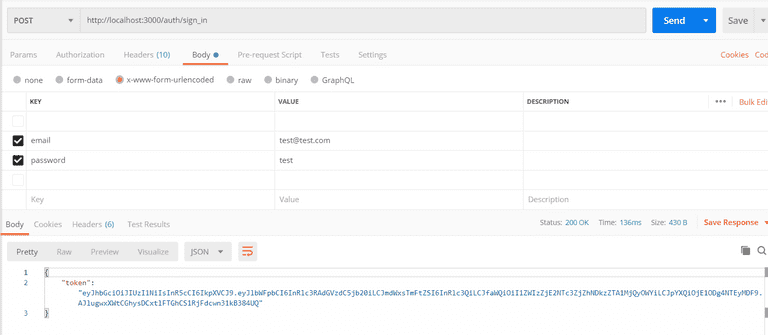
Step 11. After this, let’s sign with this URL localhost:3000/auth/sign_in . Enter the keys and values for email and password
Under the value, add JWT and the token with a space between, like so:
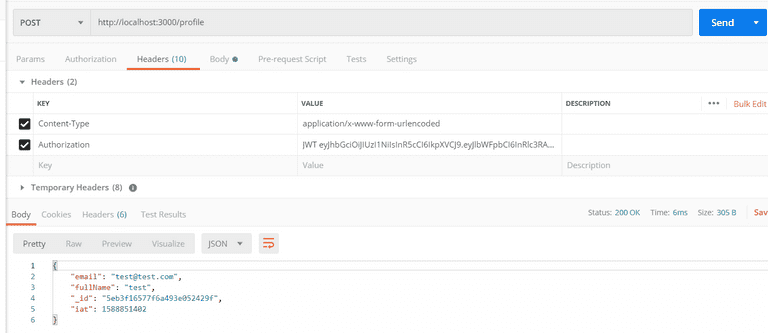
JWT eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJlbWFpbCI6Im9sYXR1bmRlZ2FydWJhQGdtYWlsLmNvbSIsImZ1bGxOYW1lIjoiT2xhdHVuZGUgR2FydWJhIiwiX2lkIjoiNThmMjYzNDdiMTY1YzUxODM1NDMxYTNkIiwiaWF0IjoxNDkyMjgwMTk4fQ.VcMpybz08cB5PsrMSr25En4_EwCGWZVFgciO4M-3ENEStep 11. Then, enter the parameters for the key and value for fetching the profile. You want to create as shown below and send:
As we have seen it is fairly easy to build a JWT authentication system with NodeJS, You can found the complete code used in this tutorial here.
Source : https://www.loginradius.com/blog/engineering/nodejs-and-mongodb-application-authentication-by-jwt/

No comments:
Post a Comment