Consider an -element array, , where each index in the array contains a reference to an array of integers (where the value of varies from array to array). See the Explanation section below for a diagram.
Given , you must answer queries. Each query is in the format i j, where denotes an index in array and denotes an index in the array located at . For each query, find and print the value of element in the array at location on a new line.
Click here to know more about how to create variable sized arrays in C++.
Input Format
The first line contains two space-separated integers denoting the respective values of (the number of variable-length arrays) and (the number of queries).
Each line of the subsequent lines contains a space-separated sequence in the format k a[i]0 a[i]1 … a[i]k-1 describing the -element array located at .
Each of the subsequent lines contains two space-separated integers describing the respective values of (an index in array ) and (an index in the array referenced by ) for a query.
Constraints
- All indices in this challenge are zero-based.
- All the given numbers are non negative and are not greater than
Output Format
For each pair of and values (i.e., for each query), print a single integer that denotes the element located at index of the array referenced by . There should be a total of lines of output.
Sample Input
2 2
3 1 5 4
5 1 2 8 9 3
0 1
1 3
Sample Output
5
9
Explanation
The diagram below depicts our assembled Sample Input:
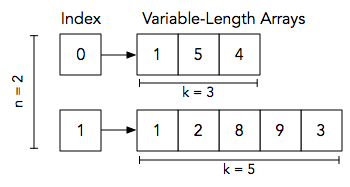
We perform the following queries:
- Find the array located at index , which corresponds to . We must print the value at index of this array which, as you can see, is .
- Find the array located at index , which corresponds to . We must print the value at index of this array which, as you can see, is .
Solution
Source : HackerRank

No comments:
Post a Comment